The Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment (QMRA) by KWB. Tool is an online simulation instrument designed to evaluate the microbial risks to human health in various water reuse scenarios. Developed with guidance from international standards such as those of the World Health Organization (WHO), the tool supports evidence-based decision-making in the planning and operation of water reuse systems.
Purpose and Target Users
The QMRA Tool is intended for a broad range of users involved in water management and safety, including water utility professionals, engineers, researchers, public health specialists, and decision-makers. It is particularly useful for those planning or managing systems where treated water is reused – for example, for irrigation, industrial purposes, toilet flushing, or even drinking water under controlled conditions.
When and How It Is Used
The tool can be applied at two critical stages of a water reuse project.
In the planning phase, it helps evaluate whether a proposed water treatment scheme can reduce microbial risks to acceptable levels. This assists users in choosing a suitable water source for a specific end use or, conversely, determining the safest end use for a given source of reclaimed water.
During the operational phase, the tool allows users to assess whether an existing treatment system continues to meet safety targets. Here, users can input site-specific data – such as pathogen concentrations, removal efficiencies of each treatment step, and realistic exposure scenarios – to generate a tailored risk profile.
It is important to note that the QMRA Tool is not a design tool for treatment plants, but rather a tool for risk estimation.
How the Tool Works
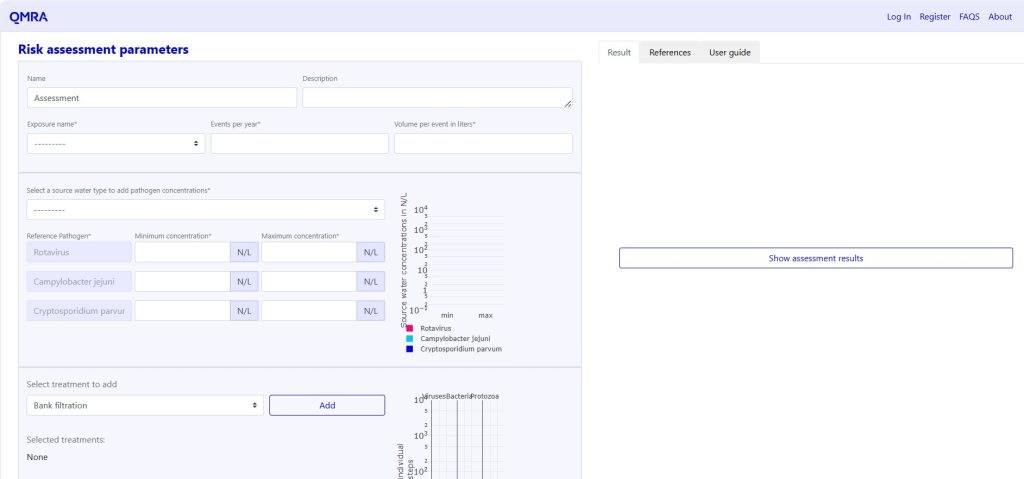
The tool can be used with default values sourced from scientific literature and international guidelines or with custom data from specific projects. Users input parameters including:
- The type of exposure scenario (e.g. irrigation, toilet flushing),
- Frequency and volume of exposure events,
- Concentrations of key reference pathogens in source water (e.g. rotavirus, Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium parvum),
- Log removal values (LRVs) of different treatment processes for viruses, bacteria, and protozoa.
Based on these inputs, the tool simulates the annual risk of infection and calculates the associated disease burden using Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) – a metric indicating the loss of healthy life years. These outcomes are then compared against WHO’s recommended thresholds: no more than one infection per 10,000 people per year or one micro-DALY (10⁻⁶ DALY) per person per year.
What Types of Risks Are Evaluated?
The QMRA Tool focuses on microbial risks, particularly those associated with pathogens originating from faecal contamination. It considers key groups of organisms:
- Bacteria such as E. coli and Campylobacter jejuni,
- Viruses like norovirus, rotavirus, and adenovirus,
- Protozoa including Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
These pathogens are selected based on their relevance to public health and also due to their representativeness and the data availability instead of this point.
Strengths and Limitations
One of the tool’s main strengths is its ability to provide a structured and transparent risk assessment for different water reuse configurations. The tool is particularly valuable for testing different “what-if” situations and comparing the effectiveness of various treatment trains.
However, like any modelling tool, it comes with simplifications. For example, the tool assumes constant removal efficiency (LRV) for each treatment step, regardless of the sequence or operational variability. Real-world factors such as filtration rates or contact time in disinfection processes are not explicitly modelled. Therefore, while the tool provides helpful risk estimates, its results should be interpreted in conjunction with site-specific expertise and further analysis.
Conclusion
The QMRA Tool is a practical and accessible resource for understanding and managing microbial risks in water reuse projects. It bridges the gap between scientific evidence and practical application, offering users a way to quantify potential health risks and align their practices with international safety benchmarks. Whether used for planning future reuse systems or monitoring the performance of existing ones, the QMRA Tool supports safer, more informed water management decisions.
Explore and test the tool online at www.qmra.org
Information prepared by:
Aija Neilande,
project Manager
aija.neilande@kurzemesregions.lv